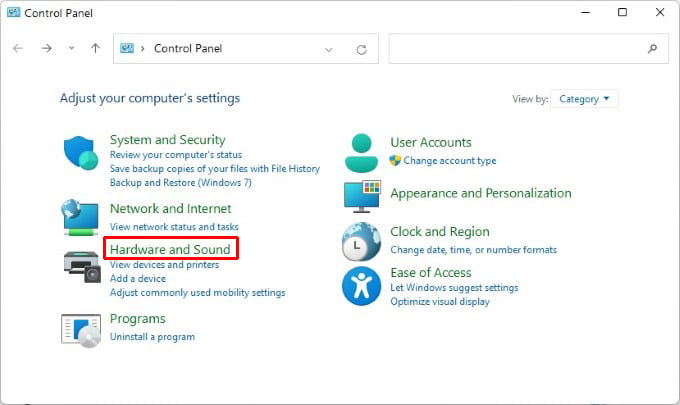
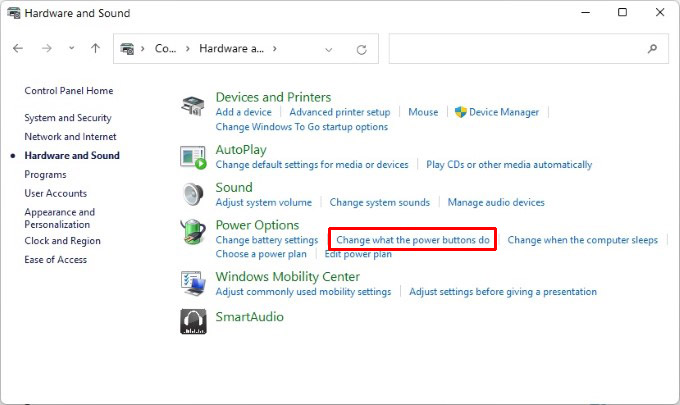
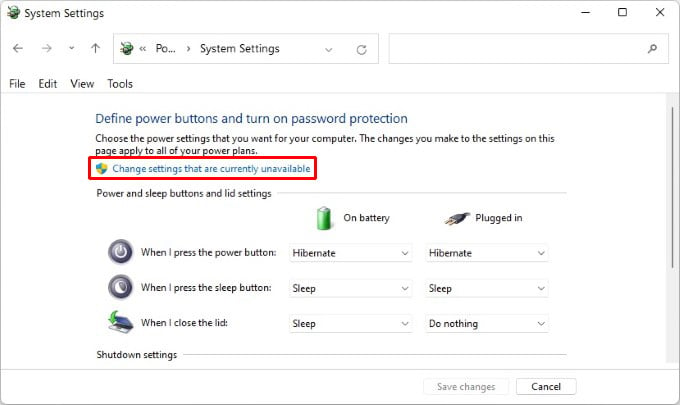
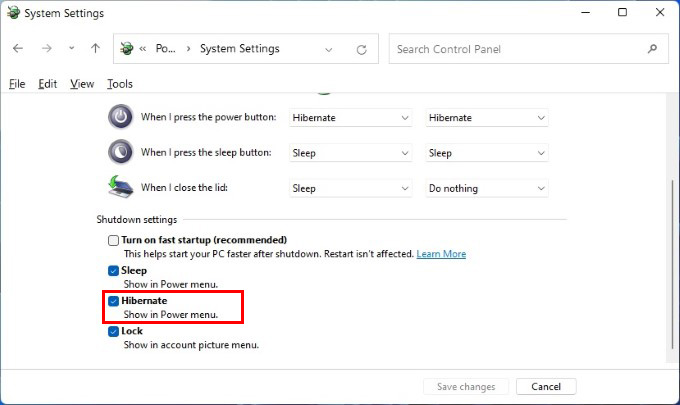
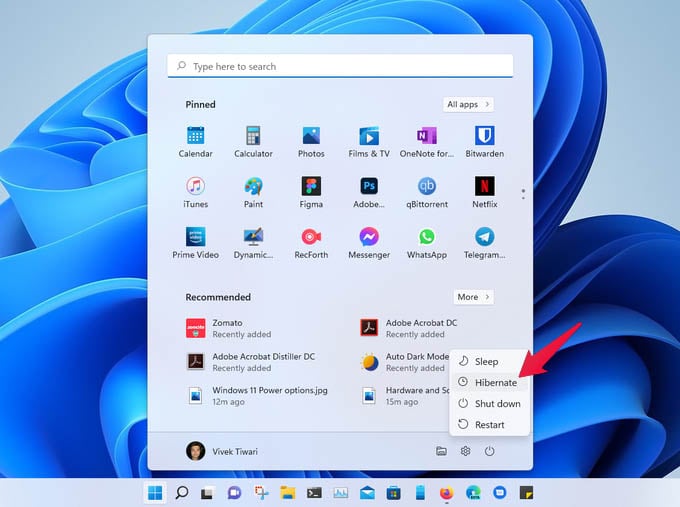
Let’s see how to fix Hibernate option missing in Windows 10 and Windows 11 PC and re-enable it in a jiffy.
Enable Hibernate in Windows 11 and Windows 10
Hibernate stores all your open documents and apps in memory so that when you turn the PC back on again you’re right where you left. It’s also faster than shutting down and turning on your PC. Hibernate is enabled by default on Windows 11, but you still won’t see it as one of the available power options in the Start menu. To enable hibernate in Windows 11 start menu, follow the steps below. This will enable hibernate in Windows 11 start menu. This is exactly the same process as Windows 10, so this will also work if you’re using a Windows 10 device. To check, just click on the Power button in the Start menu. You should see Hibernate as an option.
Hibernate vs Sleep
Hibernate saves the current state of your PC, including open documents and apps, in memory. This allows the PC to restore everything once you turn it on again. That’s practically what Sleep does, too. So you might wonder, what’s the difference? Sleep stores that information in the RAM memory. In case you didn’t know, the RAM is cleared when the PC shuts down because RAM requires power to keep things in memory. As a result, your PC stays on in Sleep mode, in a low-power state. Turning on the PC back from sleep is faster than hibernating, but your laptop battery may drain out. Hibernate stores the same system state on the hard drive or SSD. This allows the PC to shut down without losing any of the stored information about open documents and apps. So in hibernate mode, your PC is actually shut down and isn’t using any power at all. When you turn it back on, all your opened documents and windows will be present there. Sleep mode is great when you know you’ll be getting back to your work in a few hours. When you need to go to sleep, for instance, hibernate is the better choice. Hope you now have enabled the Hibernate option in your Windows PC.
Δ